
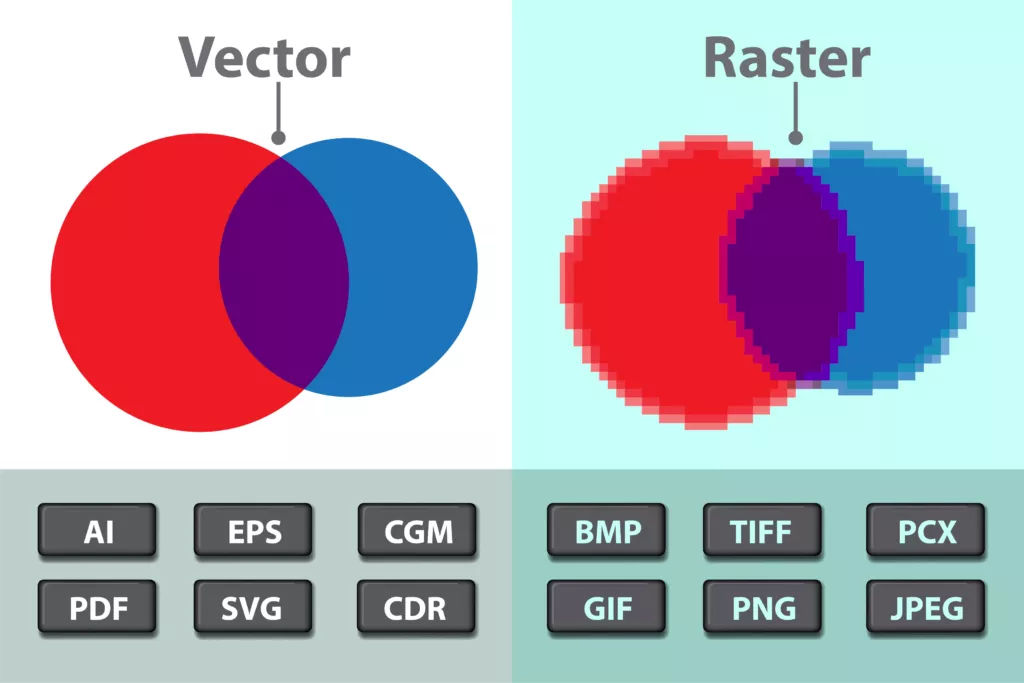
Vector images are made up of lines and curves, and they can be scaled to any size without losing any fidelity. This is one of the main reasons why vector images are often preferred for use in digital applications. This means that raster images can take up a lot of space on digital devices and storage systems. Raster images are made up of tiny pixels, and each pixel contains a color value. This makes vector images ideal for applications like logos and illustrations, where it is important to maintain a high level of quality regardless of how the image is sized. In contrast, vector images are composed of mathematical equations that describe points in space, and they can be scaled up or down without losing any detail. This is because each pixel in a raster image represents a fixed amount of data, and when the image is enlarged, the pixels become stretched out and distorted.Īs a result, the overall quality of the image decreases. Raster images are ‘resolution dependent.’ What does this mean? As anyone who has ever tried to enlarge a small image knows, raster images can quickly become blurry or pixelated when they are increased in size. Raster images can be blurry or pixelated when enlarged
WHICH ARE USED TO CREATE A RASTER IMAGE PROFESSIONAL
TIFF files are often used by professional photographers because they offer high image quality and a wide range of compression options. However, they offer high image quality and are well-suited for desktop applications. pngīMP files are generally large and uncompressed, making them unsuitable for use on the web. PNG files are similar to GIF files in many ways, but they offer a few advantages, such as the ability to include transparency information and support for a wider range of colours. GIF files are also well-suited for animation. GIF files are often used for logos and other simple graphics, because they can create small files with limited colour palettes. However, JPEG files are not as well-suited for line drawings or other types of detailed images. JPEG files are typically used for photographs, because they can create small files that retain a high level of image quality. Each of these file types has its own strengths and weaknesses, and you may find that one is better suited for your needs than the others.

The five most common raster file types are JPEG, GIF, PNG, BMP, and TIFF.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Luminosityboxannotated-71d0cdaeccc34896a6efb1ccf043a04c.jpg)
Learn more about image file formats for both vector and raster images. Otherwise, a raster graphic will suffice. If you’re not sure which format to use for your next project, just remember: if you need to resize the graphic frequently, go with a vector. The five most common vector formats are AI, EPS, PDF, and SVG. Because vector images are composed of geometric shapes, they can be edited and manipulated to change their appearance without becoming "blocky" or "pixelated." Additionally, because vector images are composed of mathematical formulas rather than pixels, they can be enlarged or reduced in size without losing any quality. Vector files are often used in graphic design for illustrations and logos, as well as in other applications where a high-resolution image is not needed. The five most common raster formats are JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, and TIFF.Ī vector image is a digital image that is composed of geometric shapes, such as points, lines, and curves. Because of the way they are stored, raster images can sometimes appear "blocky" or "pixelated" when they are enlarged. Raster images are often used in digital photography, as well as in web design and other applications where a high-resolution image is needed. Pixels are the smallest individual unit of a raster image, and each pixel contains colour information that is used to generate the final image.

Rasters are a type of image that is stored in a computer as an array of tiny squares, or pixels. If you’re reading this, there’s a good chance you work with digital images in some way – and if that’s the case, then you need to know about raster images.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
